A city in northwestern Bangladesh, which lies on the Punarbhaba River. The city is bounded on the north by Suihari, Katapara, Bangi Bechapara, Pulhat, Koshba on the south, and on the east of Sheikhupura. The city is the district headquarters of Dinajpur district which is situated in Rangpur Division. Dinajpur is actually the largest district among all 16 northern districts in BD.
The economy is based mostly on agriculture production There is a well-known proverb about Dinajpur – ‘paddy piled up high, sheds full of cows, ponds brimming with fish’ [gola bhora dhan, goyal bhora goru, pukur bhora mach].
Dinajpur is also famous for rice production, as Katharivog rice is one of the best-produced rice in BD. The district is also rich in its wheat production. The Lychee fruit of Dinajpur is considered
the best in BD. The main industries of Dinajpur include rice, wheat, jute, textile, sugar, and lumber, but it is also highly rich with natural resources like coal, which 3 of the 5 coal field discovered in BD are in Dinajpur.
The literary rate of the city is 85.05% which is high compared to other cities in the northern part of BD, and over the last 25 years, Dinajpur has attracted some prominent educational institutions such as Hajee Mohammad Danesh Science and Technology University and M Abdur Rahim Medical College.
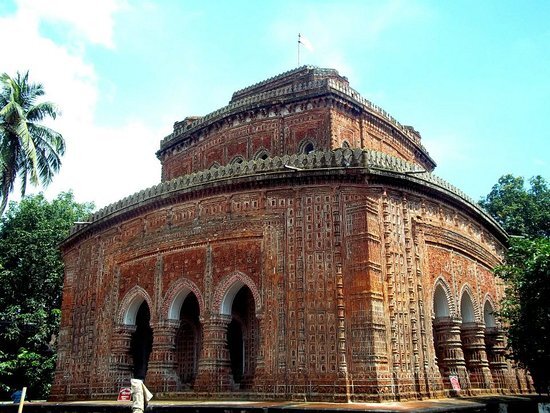

In the census of 2011, it’s estimated that 77.83% are Muslim, 19.74 are Hindu, 1.09% are Christian and 1.31%. In terms of population, the same census states that the district has 2,642,850 people. 1,363,892 males and 1,278,958 being females. Some of the tribal communities residing in Dinajpur includes Santals, Oraon, Mahali, Malpahari, and Kol tribes. Dinajpur was once a part of the ancient state of Pundravardhana. Devkot which rotated as the capital of Lakhnauti was located south of Dinajpur town, and is also called “City of Maharajas
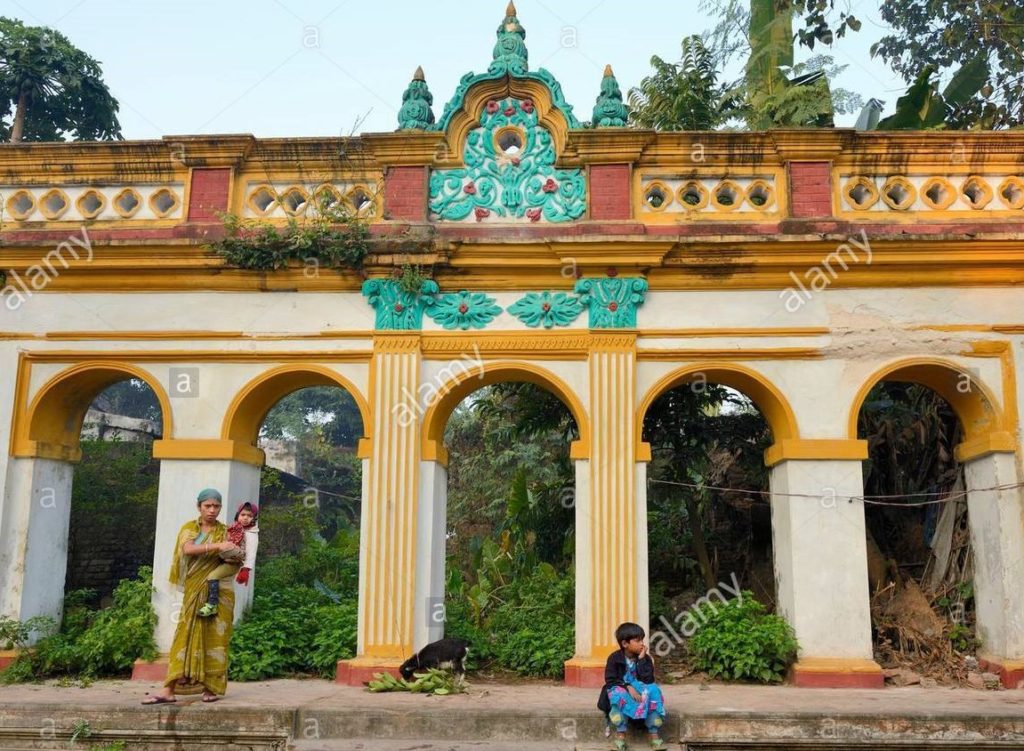

An ancient engraved stone, believed to be from the Gupta era, was recovered from the bank of a pond near Sura Masjid in the Ghoraghat Upazila in Dinajpur on
October 8. During the British Colonial period, they established rule in 1786, and was considered the biggest administrative district of undivided Bengal.
The district Dinajpur in British times included a greater portion of Bagura. Malda and parts of Rajshahi, Rangpur, and Purnea.

At first, after its formation in 1856, the Dinajpur Municipality used to be run by a town committee presided over by the Deputy Magistrate. At the time of Partition of India in 1947, part of greater Dinajpur district was included in West Bengal and it was named West Dinajpur district. People of the district took part in the Tebhaga Movement and also had significant contribution in the War of Liberation of 1971.